Vectors and Matrices¶
Vectors¶
A vector has magnitude (size) and direction
Use NumPy to create a one-dimensional array
Vector can be created as row or column using NumPy
See More
https://www.mathsisfun.com/algebra/vectors.html
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euclidean_vector
# Load NumPy Library
import numpy as np
# Create a vector as row
vector_row = np.array([1, 2, 3])
print(vector_row)
# Create a vector as column
vector_column = np.array([[1], [2], [3]])
print(vector_column)
Matrix¶
In mathematics, a matrix is a rectangular array of numbers, symbols, or expressions, arranged in rows and columns
Rows tun horizontally and columns run vertically
Use NumPy to create a two-dimensional array

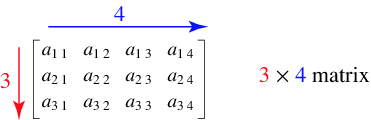
Matrix Order¶
You can think of an \(r x c\) matrix as a set of r row vectors, each having c elements; or you can think of it as a set of c column vectors, each having r elements.
The rank of a matrix is defined as (a) the maximum number of linearly independent column vectors in the matrix or (b) the maximum number of linearly independent row vectors in the matrix. Both definitions are equivalent.
If r is less than c, then the maximum rank of the matrix is r.
If r is greater than c, then the maximum rank of the matrix is c.
See More
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Matrix_(mathematics)
https://mathworld.wolfram.com/Matrix.html
https://stattrek.com/matrix-algebra/matrix-rank.aspx
Create a matrix using matrix()¶
Returns a matrix from an array type object ir string of data.
Syntax:
np.matrix(data)
mat1 = np.matrix("1, 2, 3, 4; 4, 5, 6, 7; 7, 8, 9, 10")
print(mat1)
Create a using array()¶
Returns a matrix
Syntax:
np.array(object)
mat2 = np.array([[1, 2], [3,4], [4, 6]])
print(mat2)
Matrix Properties¶
Shape¶
Returns number of rows and columns from a matrix
Syntax:
mat.shapeshape[0] - returns the number of rows
shape[1] - returns the number of columns
mat3 = np.matrix("1, 2, 3, 4; 4, 5, 6, 7; 7, 8, 9, 10")
# shape
mat3.shape
# rows
mat3.shape[0]
# columns
mat3.shape[1]
Size¶
Returns the number of elements from a matrix
Syntax:
array.size
mat4 = np.matrix("1, 2, 3, 4; 4, 5, 6, 7; 7, 8, 9, 10")
# size
mat4.size
Modifying matrix using insert()¶
Adds values at a given position and axis in a matrix
Syntax:
np.insert(matrix, object, values, axis)matrix - input matrix
object - index position
values - matrix of values to be inserted
mat5 = np.matrix("1, 2, 3, 4; 4, 5, 6, 7; 7, 8, 9, 10")
print(mat5)
# adding a new matrix `col_new` as a new column to mat5
col_new = np.matrix("1, 1, 1")
print(col_new)
# insert at column
mat6 = np.insert(mat5, 0, col_new, axis=1)
print(mat6)
# adding a new matrix `row_new` as a new row to mat5
row_new = np.matrix("0, 0, 0, 0")
print(row_new)
# insert at row
mat7 = np.insert(mat5, 0, row_new, axis=0)
print(mat7)
Modifying matrix using index¶
Elements of matrix can be modified using index number
Syntax::
mat[row_index, col_index)
mat_a = np.matrix("1, 2, 3, 4, 5; 5, 6, 7, 8, 9; 9, 10, 11, 12, 13")
print(mat_a)
# change 6 with 0
mat_a[1, 1] = 0
# show mat_a
print(mat_a)
# extract 2nd row
mat_a[1, :]
# extract 3rd column
mat_a[:, 2]
# extract elements
mat_a[1, 2]
Matrix Operations¶
A = np.arange(0, 20).reshape(5,4)
print(A)
B = np.arange(20, 40).reshape(5,4)
print(B)
Addition¶
np.add()- performs element-wise addition between two matricesSyntax:
np.add(matrix_1, matrix_2)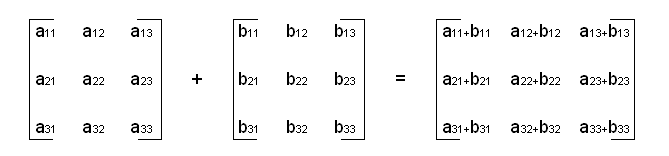
# addition
np.add(A, B)
Subtraction¶
np.subtract()- performs element-wise subtraction between two matrices.Syntax:
np.subtract(matrix_1, matrix_2)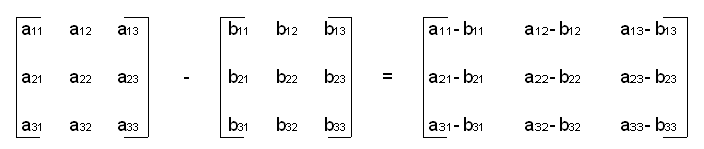
Transpose¶
np.transpose()- Permute the dimensions of an array.Transposing an \(M \times N\) matrix flips it around the center diagonal and results in an \(N \times M\) matrix.
Syntax:
np.transpose(matrix)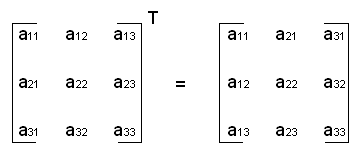
A = np.arange(0, 20).reshape(5,4)
print(A)
# transpose
np.transpose(A)
Multiplication¶
np.dot()- performs matrix multiplication between two matrices.Syntax:
np.dot(matrix_1, matrix_2)
# multiplication
np.dot(A,B)
Note
For matrix multiplication the number of columns in matrix \(A\) should be equal to the number of rows in matrix \(B\)
Here, Order of matrix \(A\) = \(5 \times 4\) and order of matrix \(B\) = \(5 \times 4\)
So, \(5 \neq 4\)
That’s why it shows ValueError: shapes (5,4) and (5,4) not aligned: 4 (dim 1) != 5 (dim 0)
# transpose matrix B to make it 4x5 in dimension
T = np.transpose(B)
print(T)
# now we can perform multiplication
np.dot(A,T)
# using matmul
np.matmul(A, T)
# using @ operator
A @ T
Element-wise multiplication¶
np.multiply()- performs element-wise multiplication between two matrices.Syntax:
np.multiply(matrix1, matrix2)
# element-wise multiplication
np.multiply(A, B)
Division¶
np.divide()- performs element-wise division between two matrices.Syntax:
np.divide(matrix_1, matrix_2)
# division
np.divide(A, B)