Introduction to NumPy¶
What is NumPy?¶
NumPy is a Python package which stands for ‘Numerical Python’.
It is the core library for scientific computing, which contains a powerful n-dimensional array object.
Provide tools for integrating C, C++ etc.
It is also useful in linear algebra, random number capability etc.
Sophisticated (broadcasting) functions
Tools for integrating C/C++ and Fortran code
Useful linear algebra, Fourier transform, and random number capabilities
NumPy array can also be used as an efficient multi-dimensional container for generic data.
Keypoints¶
NumPy arrays have a fixed size at creation, unlike Python lists(which can grow dynamically).
Changing the size of an
ndarraywill create a new array and delete the original.The elements in a NumPy array are all required to be of the same data type and thus will be the same size in memory(Homogenous)
NumPy arrays facilitate advance mathematical and other types of operations on large numbers of data(Faster)
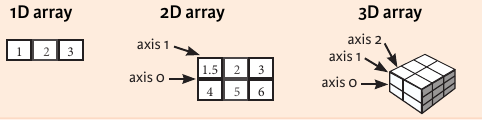
NumPy Array¶
Numpy array is a powerful N-dimensional array object which is in the form of rows and columns. We can initialize numpy arrays from nested Python lists and access it elements. In order to perform these numpy operations.
NumPy Ecosystem¶
statsmodel Estimate statistical models, and performs tests.
scikit-image Collection of algorithms for image processing.
scikit-learn Simple and efficient tools for machine learning
pandas Data Analysis and manipulation.
matplotlib Plotting library for 2D graphs and visualizations.
Why Numpy?¶
Less Memory
Fast
Convenient
Why NumPy is Fast?¶
Vectorization
Vectorization describes the absence of any explicit looping, indexing etc; in the code-these things are taking place, of course, just behind the scenes in optimized, pre-compiled C code.
Broadcasting
The term broadcasting describes how NumPy treats arrays with different shapes during arithmetic operations. Subject to certain constrains, the smaller array is “broadcast” across the larger array so that they have compatible shapes.